Solwer’s Copyleft Tool
What is Copyleft?
Copyleft is a licensing concept used primarily in the world of software and creative works. It ensures that a work (like a program, document, or design) remains free and open for anyone to use, modify, and distribute — but with a key condition: any derivative work must also be distributed under the same Copyleft terms.
Here’s how it works:
- You can use it freely: Anyone can use, modify, and share the original work.
- You must share alike: If you modify the work or build upon it, you must release your version under the same copyleft license.
- It protects openness: This prevents someone from taking a free work, modifying it, and then making it proprietary.
Key Copyleft Licenses:
| License | Type | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| GPL (General Public License) | Strong copyleft | Requires derivative works to be GPL-licensed |
| AGPL (Affero GPL) | Strong copyleft | Extends GPL to networked software (e.g., SaaS) |
| LGPL (Lesser GPL) | Weak copyleft | Allows linking with proprietary software |
| CC BY-SA (Creative Commons ShareAlike) | Copyleft for creative works | Requires same license for derivatives |
Copyleft vs. Copyright
- Copyright restricts usage unless permission is granted.
- Copyleft uses copyright law to enforce openness and freedom.
Real-World Examples
Example 1: Linux Kernel (GPL-2.0)
- Use case: Embedded systems, servers, Android OS.
- Implication: Any modifications to the kernel must be released under GPL-2.0.
Example 2: WordPress (GPL-2.0)
- Use case: Website CMS.
- Implication: Themes and plugins that are derivative works must also be GPL-compliant.
Example 3: Proprietary Software Using GPL Code
- If a company embeds GPL-licensed code into its proprietary software and distributes it, it must release its entire source code under GPL — which many companies avoid.
Copyleft vs. Permissive Licenses:
| Feature | Copyleft (e.g., GPL) | Permissive (e.g., MIT, Apache) |
|---|---|---|
| Redistribution | Must be same license | Can be any license |
| Commercial Use | Allowed, but with conditions | Freely allowed |
| Proprietary Integration | Not allowed | Allowed |
| Source Code Disclosure | Required | Not required |
Solwer’s Copyleft Tool – Dependency License Scanner
This is a powerful tool available to help you detect and manage copyleft licenses in your codebase. This tool is essential for ensuring compliance and avoiding legal risks when using open-source software.
You can access the free tool by clicking here Copyleft Scanner . Below is a step-by-step guide to using the Dependency Scanner.
Step 1. Open the link to see the screen below.
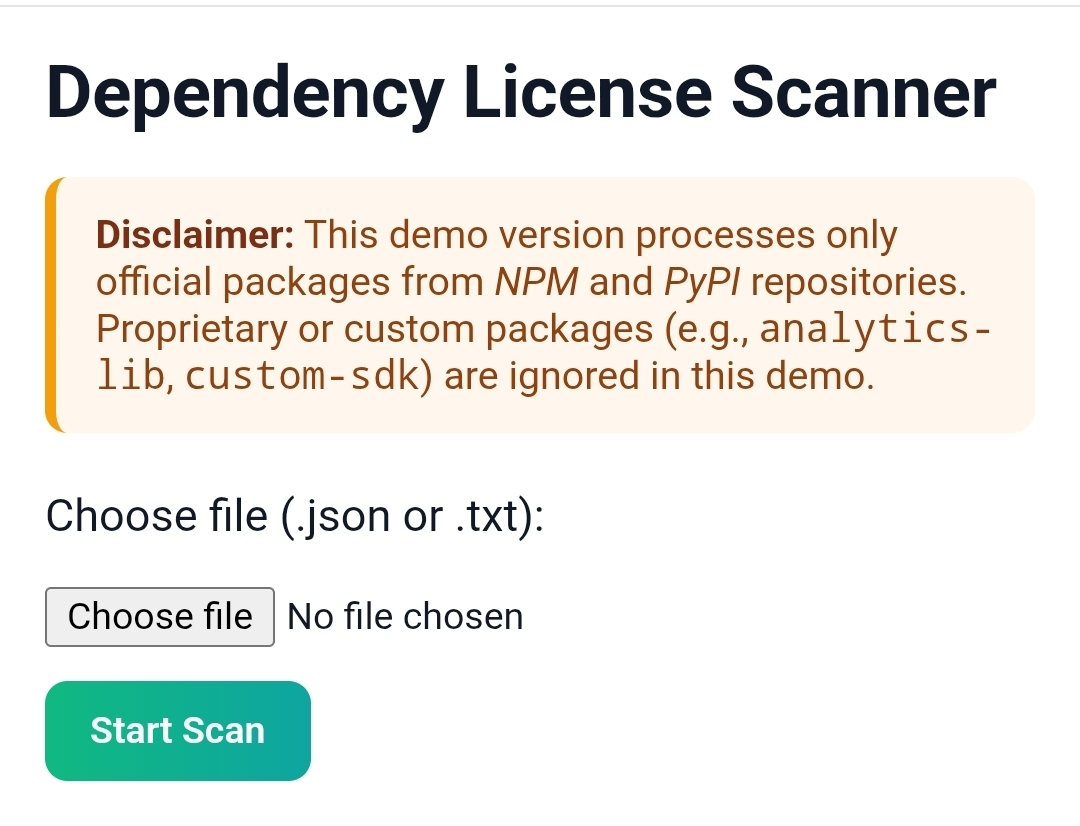
Step 2. Click on Choose File to upload either a .json file or a .txt file.
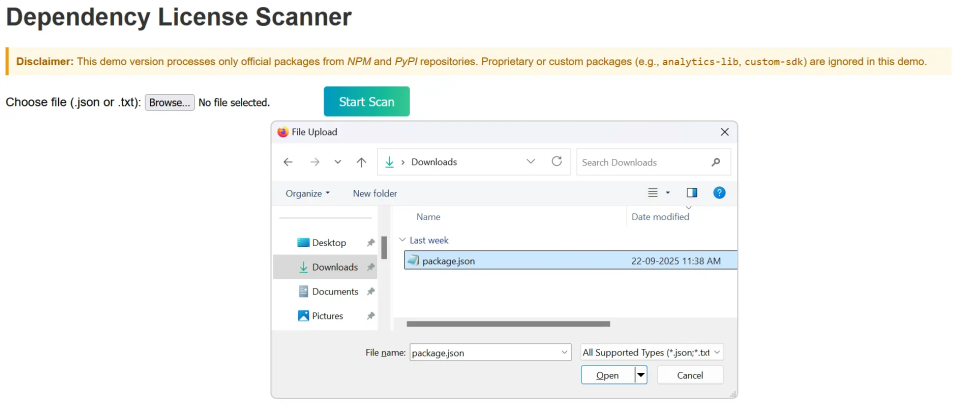
Step 3. Once the file has been uploaded, click on Start Scan.

Step 4. Depending on the file size, the tool will take a couple of seconds to finish the scan and the progress is shown as below.
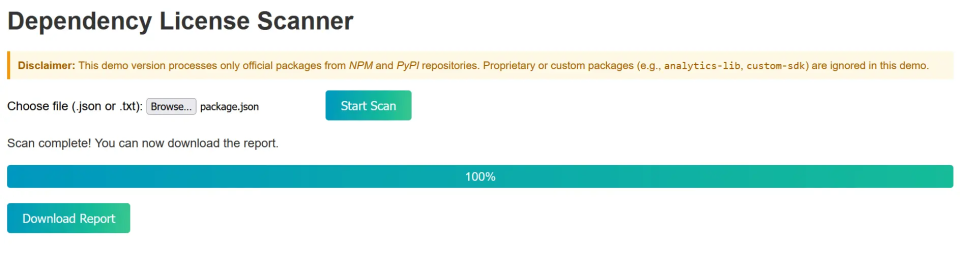
Step 5. Once the progress reaches 100%, you can then download the report. Click on Download Report.
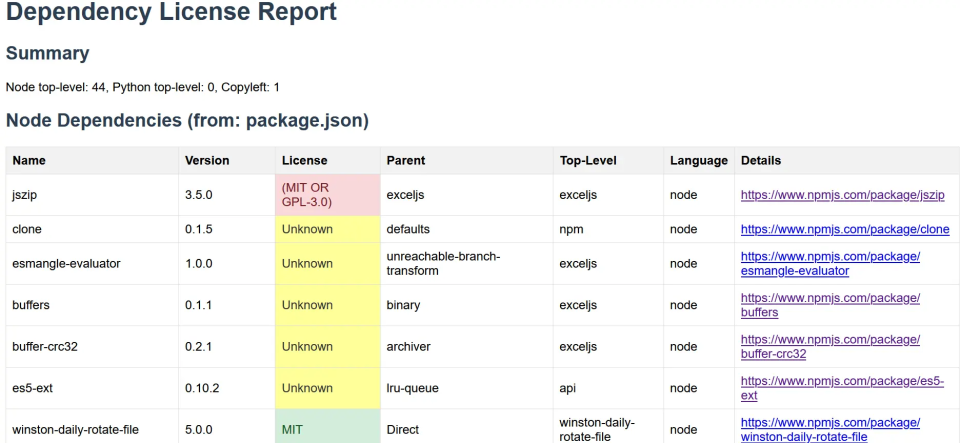
This is a sample of how the downloaded report will look like. As you can see there are three colour codes used in the report.
- Red – you need to check this as there might be a copyleft concern with that library
- Yellow – results unknown. Needs to be checked manually
- Green – safe to use
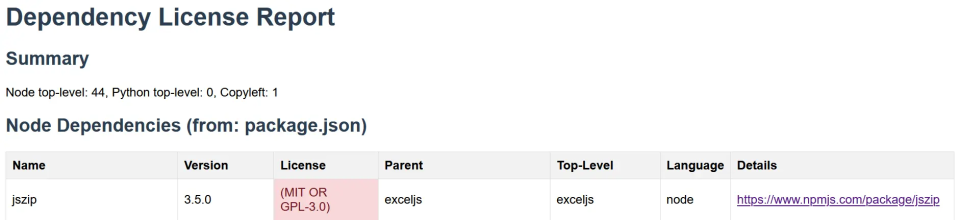
Step 6. Let’s look at the first one highlighted in Red. Here the license is mentioned as MIT or GPL 3.0. A quick online search will show us that the MIT library is safe to use. In case the result shows only GPL, you will need to change the parent library to avoid Copyleft concerns.
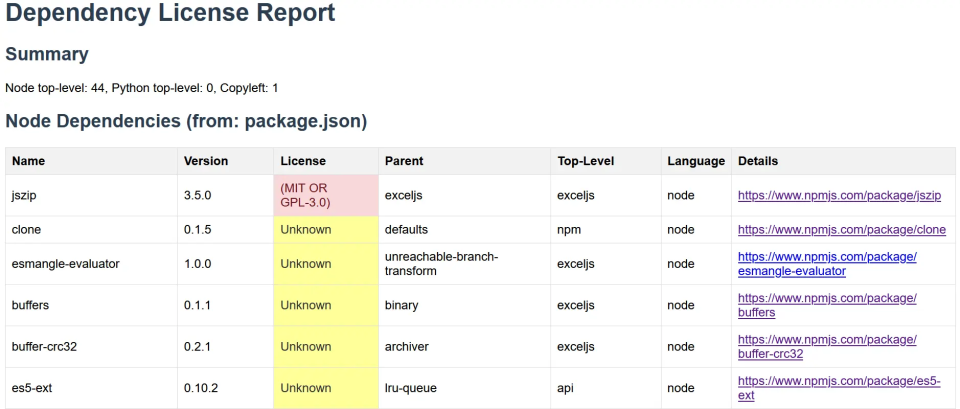
To research about the ones highlights in Yellow, click on the links provided next to that particular library.
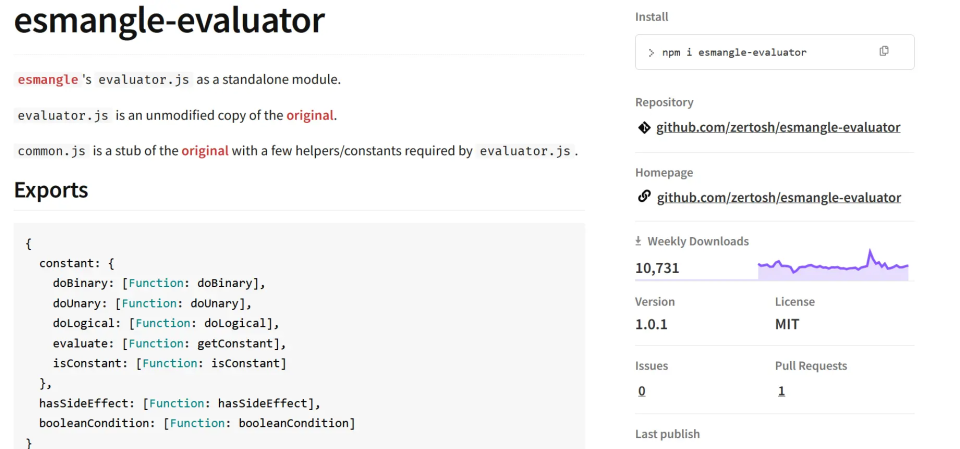
When you click on the link for the second line item, esmangle evaluator, you will see that it comes under the MIT license which is safe to use. The same has been shown in the image below.
Summary Overview
- Node top-level dependencies: 44
- Python top-level dependencies: 0
- Copyleft licenses detected: 1
Copyleft Concern
- Package: jszip@3.5.0
- License: (MIT OR GPL-3.0)
- Implication: This is a dual-licensed package. If you choose the GPL-3.0 option, your project must comply with its strong copyleft terms — meaning you’d need to open-source your entire project under GPL if you distribute it.
- Safe path: You can choose the MIT option to avoid copyleft obligations, assuming no other GPL-only dependencies are present.
Unknown Licenses:
Several packages have unknown licenses, which is a potential risk
| Package | Version | Parent Module |
|---|---|---|
| esmangle-evaluator | 1.0.0 | unreachable-branch-transform |
| buffer-crc32 | 0.2.1 | archiver |
| buffers | 0.1.1 | binary |
| clone | 0.1.5 | defaults |
| es5-ext | 0.10.2 | lru-queue |
- These packages don’t clearly declare their license, which can lead to legal ambiguity.
- You may need to manually check their license on npmjs.com or GitHub to confirm compliance.
Recommendations
-
Choose MIT for jszip unless you intentionally want GPL-3.0
-
Investigate unknown licenses to ensure they’re not copyleft or restrictive
Explore more
The Basics of Vehicle Digital Inspection: What It Is and How It Works
Discover how digital transformation is revolutionizing vehicle inspection processes, improving efficiency, accuracy, and compliance while reducing costs and environmental impact.
India's Logistics Challenges: Understanding the Roadblocks and the Way Forward
Explore how predictive maintenance technologies are transforming equipment management, reducing downtime, and optimizing operational efficiency in modern manufacturing.
